Thermal night vision binoculars: Insider guide to specs, use, and picks
Imagine trying to spot something in complete, total darkness. No moon, no stars, nothing. Or what about cutting through thick fog or smoke? That’s where thermal night vision binoculars come in, and they're a total game-changer.
Unlike traditional night vision that needs a little bit of light to work, thermal imaging plays by a completely different set of rules. It doesn't see light at all—it sees heat.
How You Can See Heat in Total Darkness
Most people are familiar with classic "green" night vision. Those devices are essentially light amplifiers. They take whatever tiny amount of ambient light is available—from the moon or stars—and magnify it thousands of time so you can see. But if there's zero light, they're just as blind as you are.
Thermal optics don't have that problem. They see a world that's completely invisible to our eyes.
Seeing the Invisible World of Heat
Everything around us that isn't at absolute zero gives off thermal energy. Living creatures, the ground, a recently driven truck—they all radiate heat. Thermal binoculars are built with special sensors that detect this infrared energy and translate it into a picture you can see.
Think of it this way: our eyes see a world painted in light and color. A thermal device sees a world painted in temperature. A warm-blooded animal will practically glow against the cooler background of trees and rocks. You can even see the lingering heat from footprints on the ground for a few minutes after someone has walked by. It’s an incredible advantage.
Thermal imaging gives you a massive edge in detection because it couldn't care less about darkness or camouflage. It sees an object's own heat, making it pop against its surroundings, even through smoke, dust, or fog.
The Practical Advantage in the Field
This ability to see heat signatures has some incredibly powerful real-world uses. For a hunter, it means being able to spot an animal that's perfectly still and camouflaged in the brush. For law enforcement or a security team, it means finding a suspect hiding in the woods or seeing through a smoke-filled building.
At the end of the day, thermal gives you true 24/7 capability. It works when all other optics fail, providing critical information in situations where light is either gone or completely compromised. Understanding this core difference is the key to appreciating why the technical specs we're about to cover are so important.
How Thermal Imaging Actually Works
To really get a handle on what makes thermal night vision binoculars so effective, you have to look past the high-tech exterior and understand the science powering them. These aren't just cameras that are good in low light. They see an entirely different world—a world of heat that's completely invisible to our eyes.
Everything around us that's warmer than absolute zero, from a whitetail deer to a recently driven truck engine, is constantly giving off infrared energy. This is what we call a heat signature. Your thermal binoculars are built to pick up on these tiny differences in temperature and turn them into a picture you can see.
Turning Invisible Heat Into a Visible Picture
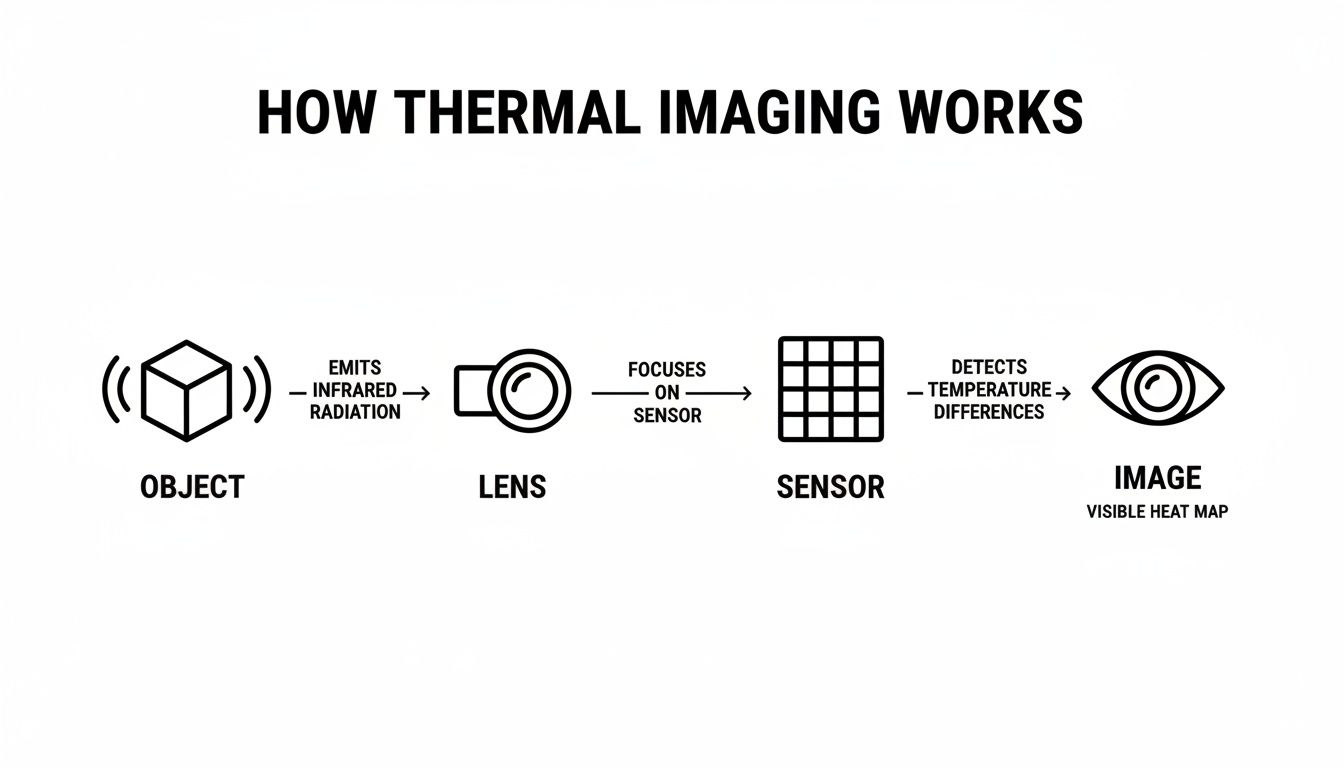
So how does it work? It all starts with the front lens, which isn't made of glass but a special material like germanium that lets infrared energy pass right through. This lens focuses that invisible heat onto a sophisticated sensor called a microbolometer.
You can think of the microbolometer as the heart of the system. Instead of capturing pixels of light like a normal camera sensor, it's a grid made up of thousands of individual points that measure temperature. Each tiny point on that grid takes a precise temperature reading from whatever you're looking at.
This is where the real magic happens. The microbolometer builds a detailed temperature map—called a thermogram—and the device’s internal brain instantly translates that data into the image you see in the eyepiece. That’s how a deer, hidden in the brush, glows white against the cool background of the trees.
This whole process—from collecting heat to showing you a picture—happens in a split second, giving you a live, dynamic map of the thermal landscape around you.
Why This Tech Is a Game-Changer
The ability to see heat signatures through things like smoke, fog, and complete darkness gives thermal imaging a massive edge. It's why the technology is absolutely dominating the night vision market, especially for military and law enforcement use.
The numbers don't lie. The global night vision market is expected to jump from USD 10.07 billion in 2026 to a staggering USD 14.44 billion by 2031. Thermal tech is the main driver here, growing at an 8.36% compound annual rate. It just works when other technologies fail. You can see more on these market dynamics and advancements on Mordor Intelligence.
This is a totally different ballgame from traditional night vision, which needs some ambient light (like starlight) to amplify. Because thermal devices are just detecting the heat that objects themselves are giving off, they have a serious advantage in the field. For a full breakdown, check out our guide on thermal imaging vs. digital vs. analog night vision.
The final image you see through the eyepiece is usually shown in different color palettes. These are just ways of representing the temperature data to make it easier for your brain to process.
- White-Hot: This is the go-to for most people. Warmer objects appear white, making them pop against a dark, cool background. It’s perfect for spotting things quickly.
- Black-Hot: The opposite of white-hot. Warm objects look black. Some operators find this is easier on the eyes, especially when you’re scanning for hours on end.
- Color Palettes: These use a spectrum of colors (reds, yellows, blues) to show different temperature levels. This can be really useful for picking out subtle heat differences that might otherwise be missed.
At the end of the day, this entire sequence happens almost instantly, giving you a clear, actionable picture of your surroundings, no matter how dark it is.
Decoding the Technical Specifications That Matter
When you first start shopping for thermal binoculars, the spec sheet can feel pretty overwhelming. It's a wall of acronyms and numbers that, on their own, don't mean much. But getting a handle on a few key metrics is what separates a smart purchase from an expensive paperweight.
These numbers aren't just for show—they directly translate into how clearly you can see, how far you can identify a target, and whether you can track something on the move without the image turning into a blurry mess. Let's break down the specs that actually impact what you see in the field.
First, here's a quick visual of how your binoculars take invisible heat and turn it into a clear picture you can actually use.
It all starts with the lens pulling in infrared energy. The sensor then reads the tiny temperature differences, and the processor turns that data into the thermal image you see on the display.
Sensor Resolution: Clarity at a Distance
If you only pay attention to one spec, make it sensor resolution. Measured in pixels just like a TV, you'll commonly see numbers like 384×288 and 640×480. Simply put, more pixels mean a sharper, more detailed image. That detail is absolutely critical for figuring out what you're looking at from far away.
Picture this: you're trying to identify an animal 300 yards out. A low-resolution sensor might just show a warm, indistinct blob. But a high-resolution 640×480 sensor can give you enough detail to see the animal's silhouette, its head, and maybe even its antlers. That's the difference between simple detection and positive identification.
NETD: The Ability to See Subtle Heat
Noise Equivalent Temperature Difference (NETD) sounds complicated, but it's really just a measure of the sensor's sensitivity. It tells you the smallest temperature difference the device can pick up, measured in millikelvins (mK). For NETD, a lower number is always better.
Think of NETD as the sensor's ability to "feel" tiny variations in heat. A device with a low NETD—anything under 40mK is excellent—can distinguish between objects with very similar temperatures. This makes it much easier to spot a deer against a warm hillside or see details through fog or high humidity.
A high NETD value (over 60mK) results in a "noisier" or grainier image, especially when the temperature contrast in the environment is low. It can turn a clear advantage into a frustrating blur.
Refresh Rate: For Smoothly Tracking Movement
The refresh rate, measured in Hertz (Hz), tells you how many times per second the image in your eyepiece updates. For thermal optics, you'll usually see rates of 30Hz or 60Hz. If you plan on looking at anything that moves, this spec is non-negotiable.
- Low Refresh Rate (Below 30Hz): A low refresh rate creates a choppy, lagging image. Trying to track a running coyote or follow a moving vehicle will feel like watching a slide show, making it nearly impossible.
- High Refresh Rate (50Hz or 60Hz): A high refresh rate delivers a smooth, fluid image that looks natural to the human eye. This is essential for maintaining situational awareness and accurately tracking fast-moving targets without getting disoriented.
For any serious application, from hunting hogs to law enforcement surveillance, 50Hz or 60Hz is the gold standard. It ensures you never lose your target because the tech can't keep up.
Key Thermal Spec Comparison
To make sense of it all, here’s a quick-reference table that shows how these key specifications play out in the real world for different users.
| Specification | What It Means | High-Performance Indicator | Impact in the Field |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensor Resolution | The number of pixels in the sensor, determining image detail. | 640×480 or higher | Provides a sharp, clear image for positive identification at longer distances. Crucial for telling a buck from a doe. |
| NETD | The sensor's sensitivity to small temperature differences. | <40 mK | Creates a crisp image with less "noise," especially in humid or foggy conditions. Helps separate a target from its background. |
| Refresh Rate | How many times per second the image updates. | 50Hz or 60Hz | Delivers smooth, lag-free viewing, which is essential for tracking moving targets like running game or vehicles. |
| Magnification/FOV | The balance between zooming in and the width of your view. | Application-specific | High magnification is for long-range ID; a wide Field of View (FOV) is for scanning large areas. The best devices balance both well. |
Understanding this table helps you prioritize what matters most for your specific needs, whether you're scanning a field for predators or conducting a search and rescue operation.
Magnification vs. Field of View: The Fundamental Tradeoff
Finally, you have to understand the push-and-pull between magnification and Field of View (FOV). Magnification is how much closer an object appears, while FOV is how wide of an area you can see. These two specs are always fighting each other.
As you crank up the magnification to see details far away, your field of view shrinks dramatically. High magnification is fantastic for identifying a stationary target at 500 yards, but a wide FOV is what you need for scanning a treeline or tracking a moving animal without losing it.
Many thermal binoculars offer a base optical magnification and a digital zoom. Be aware that digital zoom just enlarges the existing pixels, which often degrades image quality. The key is finding the right balance of a clean optical magnification and a usable FOV for your primary mission.
Matching Your Binoculars to Your Mission
Forget about finding the “best” thermal binoculars. The real question is, what’s the best model for you? The perfect set of thermals for a police officer on a tactical team will be worlds apart from what a backcountry hunter or a rancher needs to keep an eye on their property.
It's all about matching the technology to the job at hand. Before you even look at a spec sheet, picture yourself using the device. Where are you? What are you looking for? What does a successful outcome look like? Thinking this way ensures you buy a tool that gives you a real-world advantage, not just a list of impressive but irrelevant features.
For Law Enforcement and Security Professionals
When you’re tasked with protecting people and property, your gear simply has to work. For law enforcement and security teams, there's no room for compromise—performance, reliability, and sheer toughness are the name of the game.
First and foremost, these devices have to be built like a tank. They’ll be banged around in a vehicle, exposed to rain and dust, and used day in and day out. That means you need a ruggedized housing and a high IP rating—something like IP67—to guarantee it can handle whatever the environment throws at it.
Image clarity is another non-negotiable. You’re not just looking for a warm blob in the distance; you need to identify threats and gather evidence. A high-resolution sensor, 640×480 or better, gives you the fidelity to distinguish a firearm from a phone or a tool in someone’s hand from a safe standoff distance.
And in a high-stress situation, you can't be fumbling with complicated menus. The controls need to be dead simple and intuitive. Look for units with tactile buttons you can operate with gloves on, a fast boot-up time, and an ergonomic design that feels natural to hold and use under pressure.
It's no secret that thermal imaging has taken over the night vision world. In 2022, the technology accounted for a massive 41.7% of the $7.02 billion global night vision market. Binocular systems are a huge part of that growth, especially for surveillance and security where a wide field of view is critical. You can get more details on these market trends at Grand View Research.
For the Dedicated Hunter
For a hunter, a good set of thermal binoculars changes everything. It’s a complete game-changer for scouting new areas, tracking game after the shot, and making a clean recovery. Here, the focus shifts from tactical toughness to features that help you find and positively identify your target, often across wide-open country.
The most important spec to understand is the Detection, Recognition, and Identification (DRI) range. Detection is seeing a heat signature. Recognition is knowing it's a deer. Identification is seeing it’s a mature buck. You need to match a unit's DRI capabilities to the distances you typically hunt and the game you pursue.
Don't forget about weight and ergonomics. When you’re hiking miles deep into the backcountry, every ounce counts. A lightweight, compact set of thermals that rides comfortably in a chest harness is infinitely more practical than a clunky, heavy unit you’re tempted to leave in the truck.
Many modern thermals also come with features that can make a real difference in the field:
- Integrated Laser Rangefinder (LRF): Get an instant, exact distance to your target. This is absolutely critical for making an ethical shot, especially at longer ranges.
- Ballistic Calculator: Some high-end models take that range data and give you an immediate holdover solution for your scope, taking all the guesswork out of the equation.
- Video Recording: It’s not just for sharing on social media. Recording your hunt lets you review footage, analyze animal behavior, and become a better hunter.
For Outdoor Enthusiasts and Property Owners
You don't need a badge or a hunting license to appreciate the power of seeing in the dark. For homeowners with acreage, ranchers, and anyone who loves the outdoors, thermal binoculars offer incredible utility and peace of mind. To see how these tools fit into a complete night vision system, check out our guide on how thermal spotters can enhance your night vision.
For this crowd, the main job is often just detection. You want to know if something—an animal or a person—is on your land long before it gets anywhere near the house. A model with a wide field of view is perfect for sweeping large pastures, fence lines, or a dark treeline from the safety of your porch.
The applications are endless:
- Property Security: Quickly scan your land for two- or four-legged intruders.
- Search and Rescue: A thermal imager is an invaluable tool for finding a lost pet or even a person in an emergency.
- Wildlife Observation: Watch nocturnal animals in their natural habitat without spooking them with a flashlight.
For these uses, a simple, user-friendly interface and a long-lasting battery are often far more important than military-grade specs or extreme magnification.
Getting Practical: Handling, Power, and the Law
Okay, let's move past the spec sheets for a minute. The raw numbers—resolution, refresh rate, NETD—are absolutely vital, but they don't tell the whole story. A few real-world details can be the difference between a tool you love and an expensive paperweight. We're talking about how the device feels in your hands, how you keep it powered, and the serious legal rules you need to know.
Getting these details right ensures you pick a unit that's not just powerful, but also practical for your specific missions. It’s about protecting your investment and making sure you can actually use it legally and effectively.
Ergonomics and Power Solutions
Think about it: how a pair of binoculars feels after an hour of scanning the horizon is just as crucial as the image it produces. That's where ergonomics come in. A well-designed thermal optic should feel like an extension of your eyes, not a brick you're struggling to hold steady.
Keep an eye out for these design features:
- Weight and Balance: Is it front-heavy? A balanced device reduces strain on your wrists and neck, which is a lifesaver during long nights of observation or tracking. Lighter is often better, especially if you’re on the move.
- Button Placement: You need to be able to change settings without thinking. The best units have intuitive controls that you can easily find and operate in total darkness, even with gloves on.
- Grip and Housing: A solid, rubberized grip is non-negotiable for use in wet or cold weather. It also helps to have a rugged housing that can take a few bumps without damaging the sensitive electronics inside.
Just as important is what keeps the lights on. Power sources generally come in two flavors, and each has its own set of trade-offs.
| Power Type | The Good | The Bad |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Rechargeable | Super convenient—no extra batteries to buy. Often allows for a more compact and streamlined design. | Runtime is finite. When it dies, your observation is on hold until you can recharge. |
| External/Replaceable | You get unlimited runtime as long as you have spare batteries. Perfect for multi-day trips or off-grid use. | Can add bulk. You have to remember to pack and carry spare batteries (like CR123A or AA). |
Thankfully, many modern high-end units give you the best of both worlds. They'll have a built-in rechargeable battery but also feature a USB-C port, allowing you to connect an external power bank for nearly endless field use.
The Big One: Understanding ITAR and Export Rules
Pay close attention here, because this is probably the single most important legal aspect of buying high-performance thermal optics. ITAR, which stands for the International Traffic in Arms Regulations, is a set of strict U.S. government rules controlling the export of defense-related tech.
Since advanced thermal imaging is a key military technology, many of the most capable thermal binoculars fall squarely under ITAR control.
So, what does this mean for you? It's simple: high-performance thermal devices—especially those with fast refresh rates of 30Hz or 60Hz and high-resolution sensors—cannot be legally taken or shipped outside the United States without an explicit license from the U.S. Department of State.
This isn't just a rule for international customers. As a U.S. citizen, the responsibility falls on you to ensure the device never leaves the country. Selling it to a foreign national, even if they're inside the U.S., can be a serious violation. Your best bet is to always buy from a reputable, U.S.-based dealer who can walk you through the specific restrictions for the model you’re interested in.
With rising geopolitical tensions and defense modernization efforts worldwide, the demand for this controlled technology is exploding. Governments are deploying thermal optics for everything from border security to special operations, fueling massive growth in the sector. You can learn more about these trends by reviewing the global infrared NVG market projections on Research and Markets. This global context really drives home why regulations like ITAR are enforced so rigorously.
Protecting Your Investment in Thermal Optics
Let's be honest—high-quality thermal night vision binoculars are a serious piece of kit and a major financial commitment. Just like any precision instrument, they need the right care to keep them running at peak performance for years to come. A few simple habits will ensure your device is always ready to go when you need it, holding its value and reliability over the long haul.
The single most important—and delicate—part of your thermal is the objective lens. Most are made from germanium, a material that’s fantastic for letting infrared energy pass through but is also surprisingly soft. It scratches easily, so whatever you do, never wipe it with your shirt or a random cloth.
Always start cleaning with a blower bulb or a can of compressed air to get rid of any loose grit. If you don't, you're just grinding that debris into the lens. For fingerprints or smudges, use a proper lens cleaning solution and a fresh microfiber cloth, wiping in gentle, circular motions. Rubbing too hard can permanently strip the delicate anti-reflective coatings, which will ruin your image quality.
Storage and System Upkeep
How you store your gear is just as crucial as how you clean it. When you're done for the day, put the binoculars back in their protective hard case. It’s not just for show—that case is designed to shield the sensitive electronics and seals from drops, dust, and moisture.
Your thermal optic is a sophisticated piece of digital equipment. Store it in a stable, dry environment—avoid leaving it in a hot vehicle for extended periods, as extreme temperatures can degrade sensor performance and battery life over time.
Don't forget about firmware. Manufacturers are constantly pushing out updates that do more than you'd think. These updates can deliver real performance boosts, fix annoying bugs, and sometimes even add new features like better color palettes or integrated ballistic calculators. Make it a habit to check the manufacturer’s website and keep your software current. It’s the easiest way to make sure your device is running at 100%.
Finally, know your warranty and support options before you even make the purchase. A solid warranty with responsive customer service is worth its weight in gold. For any problems that go beyond basic cleaning, you need to call in the pros. You can learn more about what to look for by reading about common night vision gear issues and how repairs can help. Taking these steps isn't just maintenance; it's protecting a valuable asset.
Your Top Questions About Thermal Binoculars, Answered
As you get closer to making a decision, a few last-minute questions always seem to surface. That's completely normal. Thermal tech is a whole different ballgame compared to your standard optics, so getting straight answers is the only way to feel good about your choice. Here are some of the most common things people ask us before they buy.
Think of this as the final once-over. We want to clear up any lingering confusion and make sure you know exactly what to expect when you get these tools out in the real world.
Can These Things Actually See Through Walls or Glass?
This is probably the number one question we get, and the answer is a firm no. It's a common movie myth, but thermal energy just can't pass through solid objects like walls, concrete, or even a thick tree. What you'll see is the surface temperature of the wall itself, not what's behind it.
Glass is another no-go. Standard glass actually reflects long-wave infrared energy. If you point a thermal imager at a window, you're more likely to see a blurry, heat-based reflection of yourself than anything on the other side.
How Does Weather Mess With Performance?
Weather definitely has a say in how well your thermal device performs. While thermals cut through fog, smoke, and dust in a way that the naked eye or traditional night vision can only dream of, they aren't totally immune to mother nature.
- Humidity and Rain: A lot of moisture in the air can soak up thermal energy, which can shorten your effective range and wash out the image contrast.
- Bitter Cold: In really cold weather, the temperature gap between a warm target and the frozen background gets huge. This often leads to incredibly sharp, high-contrast images.
- Scorching Heat: On a hot day, things get tricky. Background objects like rocks and dirt soak up the sun's heat and can get close to the same temperature as your target. This shrinks the contrast and makes spotting a lot tougher.
The thing to remember is that thermal imaging isn't magic—it's just science. It all hinges on temperature differences. Any weather that evens out the temperatures across the landscape will impact the clarity of what you see in the eyepiece.
So, is Thermal Better Than Old-School Night Vision?
It's not about which is "better," but which is the right tool for the job. They're built for different things, and each one shines in its own way.
Traditional night vision, the green-glowing stuff you're used to, works by amplifying very small amounts of visible light. This gives you a really detailed picture that's fantastic for identifying exactly what you're looking at. The catch? It needs some light to function and is easily fooled by good camouflage or pitch-black shadows.
Thermal imaging, on the other hand, only cares about heat. This makes it absolutely unbeatable for pure detection, especially in zero-light situations. It also punches right through obscurants like smoke and heavy fog. For a lot of professional teams, the ultimate setup is to use both: a thermal bino to find the heat signature, then a night vision scope to get a positive ID.
Ready to own the night? The team here at Superior Tactical LLC lives and breathes this stuff. We can walk you through the options and help you find the perfect thermal night vision binoculars for your needs. Check out our hand-picked collection of professional-grade optics and get ready for your next mission. Visit us at https://superiortac.com.